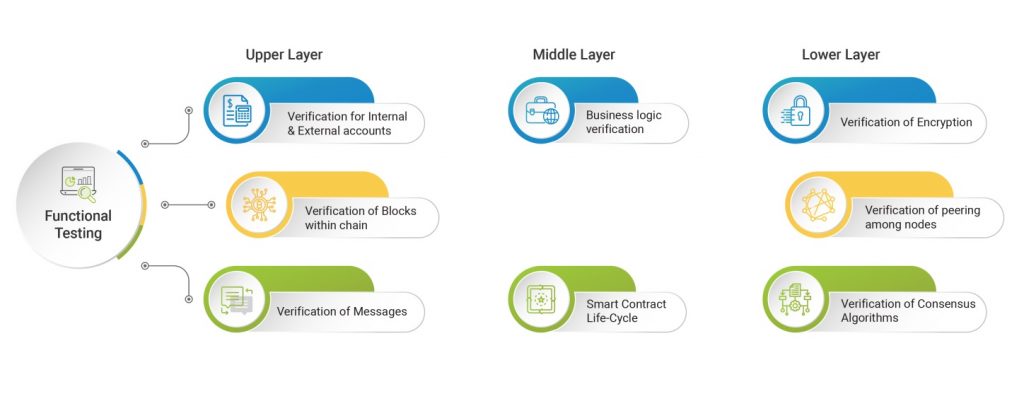
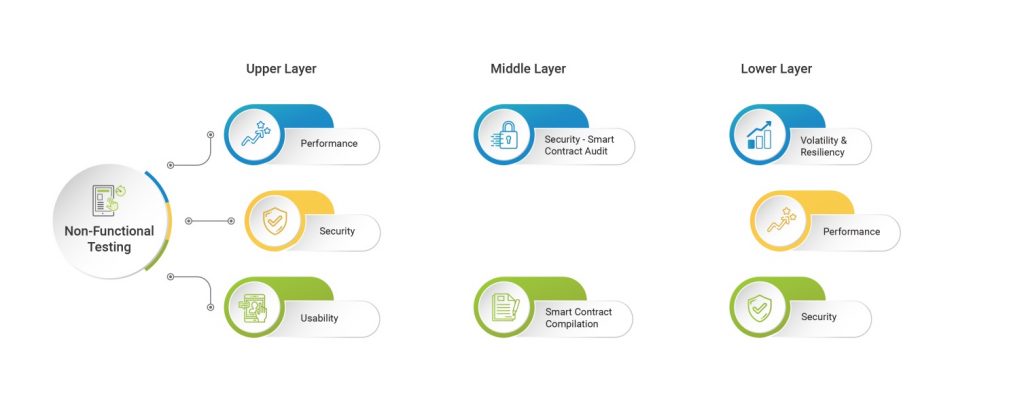
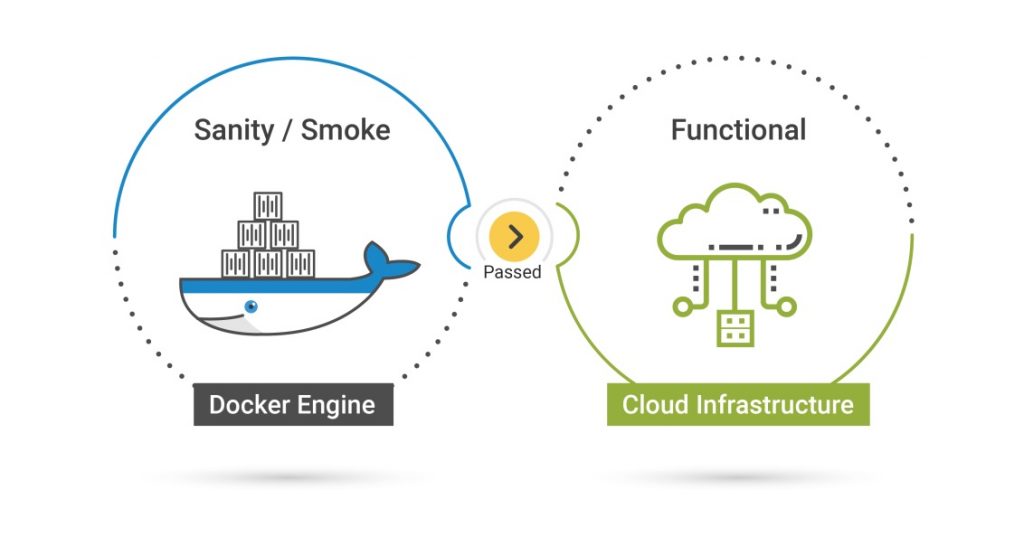
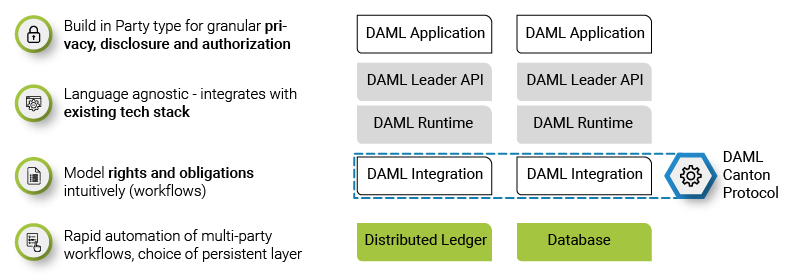
Introduction
Investment research and analysis is beginning to look very different from what it did five years ago. While five years ago, the data deluge could have confounded asset management leaders, they now have a choice on how things could be done differently, thanks to AI and advanced analytics. Advanced analytics helps create value by eliminating biased decisions, enabling automatic processing of big data, and using alternative data sources to generate alpha.
With multiple sources of data and emerging AI applications heralding a paradigm shift in the industry, portfolio managers and analysts who earlier used to manually sift through large volumes of unstructured data for investment research can now leverage the power of AI tools such as natural language processing and abstraction to simplify their task. Gathering insights from press releases, filing reports, financial statements, pitches and presentations, CSR disclosures, etc., is a herculean effort and consumes a significant amount of time. However, with AI-powered data extraction tools such as Magic DeepSight™, quick processing of large-scale data is possible and practical.
A tool like Magic DeepSight™ extracts relevant insights from existing data in a fraction of the time and capital compared to manual processing. However, the real value it delivers is by supplementing human intelligence with powerful insights, allowing analysts to direct their efforts towards high-value engagements.
Processing Unstructured Data Is Tough
There are multiple sources of information that front office analysts process daily, which are critical to developing an informed investment recommendation. Drawing insights from these sources of structured and unstructured data are challenging and complex. These include 10-K reports, the reasonably new ESG reports, investor reports, and various other company documents such as internal presentations and several PDFs. SEC EDGAR database makes it easy to access some of this data, but extracting this data from SEC EDGAR and identifying and then compiling relevant insights is still a tedious task. Unearthing insights from other unstructured documents also takes stupendous manual efforts due to the lack of any automation.
10-K Analysis using AI
More detailed than a company’s annual report, the 10-K is a veritable powerhouse of information. Therefore, accurate analysis of a 10-K report would lead to a sounder understanding of the company. There are five clear-cut sections of a 10-K report – business, risk factors, selected financial data, management discussion and analysis (MD&A), financial statements, and supplementary data, all of which are packed with value for analysts investors alike. Due to the breadth and scope of this information, handling it is inevitably time-consuming. However, two sections that usually require more attention than the others to analyze due to the complexity and existence of possible hidden anomalies are the “Risk Factors” and the “MD&A”. The “Risk Factors” section outlines all current and potential risks posed to the company, usually in the order of importance. In contrast, the “Management’s Discussion and Analysis Of Financial Condition And Results Of Operations” (MD&A) section is the company management’s perspective of the previous fiscal and future business plans’ performance.
As front-office analysts sift through multiple 10-K reports and other documents in a day, inconsistencies in analysis can inadvertently creep in.
They can miss important information, especially in the MD&A and Risk Factors sections, as they have to analyze many areas to study and more reports in the queue. Even after extracting key insights, it takes time to compare the metrics in the disclosures to a company’s previous filings and against industry benchmarks.
Second, there is the risk of human bias and error, where relevant information may be overlooked. Invariably, even the best fund managers would succumb to the emotional and cognitive biases inherent in all of us, whether confirmation bias, bandwagon effect, loss aversion, or various other biases that behavioral psychologists have formally defined. Failure to consider these issues will lead to suboptimal decisions on asset-allocation and often does.
Using AI to analyze the textual information in the disclosures made within 10-Ks can considerably cut through this lengthy process. Data extraction tools can parse through these chunks of texts to retrieve relevant insights. And a tool or platform custom-built for your enterprise and trained in the scope of your domain can deliver this information to your business applications directly. More documents can be processed in a shorter time frame, and armed with new insights, analysts can use their time to take a more in-depth learning’s untapped potential look into the company in question. Implementing an automated AI-Based system omits the human errors, allowing investment strategies to be chosen that are significantly more objective, in both their formulation and execution.
Analysing ESG Reports
Most public and some private companies today are rated on their environmental, social and governance (ESG) performance. Companies usually communicate their key ESG initiatives yearly on their websites as a PDF document. Stakeholders are studying ESG reports to assess a company’s ESG conduct. Investment decisions and brand perception can hinge on these ratings, and hence care has to be taken to process information carefully. In general, higher ESG ratings are positively correlated with valuation and profitability while negatively correlated with volatility. An increased preference for socially responsible investments is most prevalent in Gen Z and Millennial demographics. As they are set to make-up 72% of the global workforce by 2029, they are also exhibiting greater concern about organizations’ and employers’ stance on environmental and social issues. This is bringing under scrutiny a company’s value creation with respect to ethical obligations that impact the society it operates in.
Although, ESG reports are significant when it comes to a company’s evaluation by asset managers, investors, and analysts, as these reports and ratings are made available by third-party providers there is little to no uniformity in ESG reports unlike SEC filings. Providers tend to have their own methodology to determine the ratings. The format of an ESG report varies from provider to provider, making the process of interpreting and analyzing these reports complicated. For example, Bloomberg, a leading ESG data provider, covers 120 ESG indicators– from carbon emissions and climate change effects to executive compensation and rights of shareholders. Analysts spend research hours reading reports and managing complex analysis rubrics to evaluate these metrics, before making informed investment decisions.
However AI can make the entire process of extracting relevant insights easy. AI-powered data cleansing and Natural Language Processing (NLP) tools can extract concise information, such as key ESG initiatives from PDF documents and greatly reduce the text to learn from. NLP can also help consolidate reports into well defined bits of information which can then be plugged into analytical models including market risk assessments, as well as other information fields.
How Technology Aids The Process
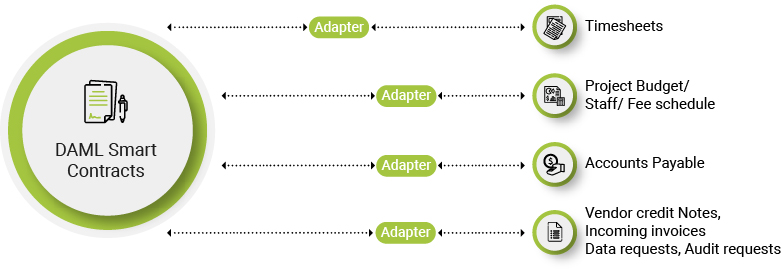
A data extraction tool like Magic DeepSight™ can quickly process large-scale data, and also parse through unstructured content and alternate data sources like web search trends, social media data, and website traffic. Magic DeepSight™ deploys cognitive technologies like NLP, NLG, and machine learning for this. Another advantage is its ability to plug the extracted information into relevant business applications, without human intervention.
About NLP and NLG
Natural Language Processing (NLP) understands and contextualises unstructured text into structured data. And Natural Language Generation (NLG) analyses this structured data and transforms it into legible and accessible text. Both processes are powered by machine learning and allow computers to generate text reports in natural human language. The result is comprehensive, machine-generated with insights that were previously invisible. But how reliable are they?
The machine learning approach that includes deep learning, builds intelligence from a vast number of corrective iterations. It is based on a self-correcting algorithm which is a continuous learning loop that gets more relevant and accurate the more it is implemented. NLP and AI-driven tools, when trained in the language of a specific business ecosystem, like asset management, can deliver valuable insights for every stakeholder across multiple software environments, and in appropriate fields.
Benefits of Using Magic DeepSight™ for Investment Research
- Reduced personnel effort
Magic DeepSight™ extracts, processes, and delivers relevant data directly into your business applications, saving analysts’ time and enterprises’ capital.
- Better decision-making
By freeing up upto 70% of the time invested in data extraction, tagging, and management, Magic DeepSight™ recasts the analysis process. It also supplements decision-making processes with ready insights.
- Improved data-accuracy
Magic DeepSight™ validates the data at source. In doing so, it prevents errors and inefficiencies from creeping downstream to other systems.
- More revenue opportunities
With reduced manual workload and emergence of new insights, teams can focus on revenue generation and use the knowledge generated to build efficient and strategic frameworks.
In Conclusion
Application of AI to the assiduous task of investment research can help analysts and portfolio managers assess metrics quickly, save time, energy and money and make better-informed decisions in due course. The time consumed by manual investment research, especially 10-K analysis, is a legacy problem for financial institutions. Coupled with emerging alternative data sources, such as ESG reports, investment research is more complicated today. After completing research, analysts are left with only a small percentage of their time for actual analysis and decision-making.
A tool like Magic DeepSight™ facilitates the research process, improves predictions, investment decision-making, and creativity. It could effectively save about 46 hours of effort and speed up data extraction, tagging, and management by 70%. In doing so, it brings unique business value and supports better-informed investment decisions. However, despite AI’s transformative potential, relatively few investment professionals are currently using AI/big data techniques in their investment processes. While portfolio managers continue to rely on Excel and other necessary market data tools, the ability to harness AI’s untapped potential might just be the biggest differentiator for enterprises in the coming decade.
To explore Magic DeepSight™ for your organization, write to us mail@magicfinserv.com or Request a Demo